The Ottawa Pest Control Journal
Educational insights into how to keep your Ottawa home or business pest free
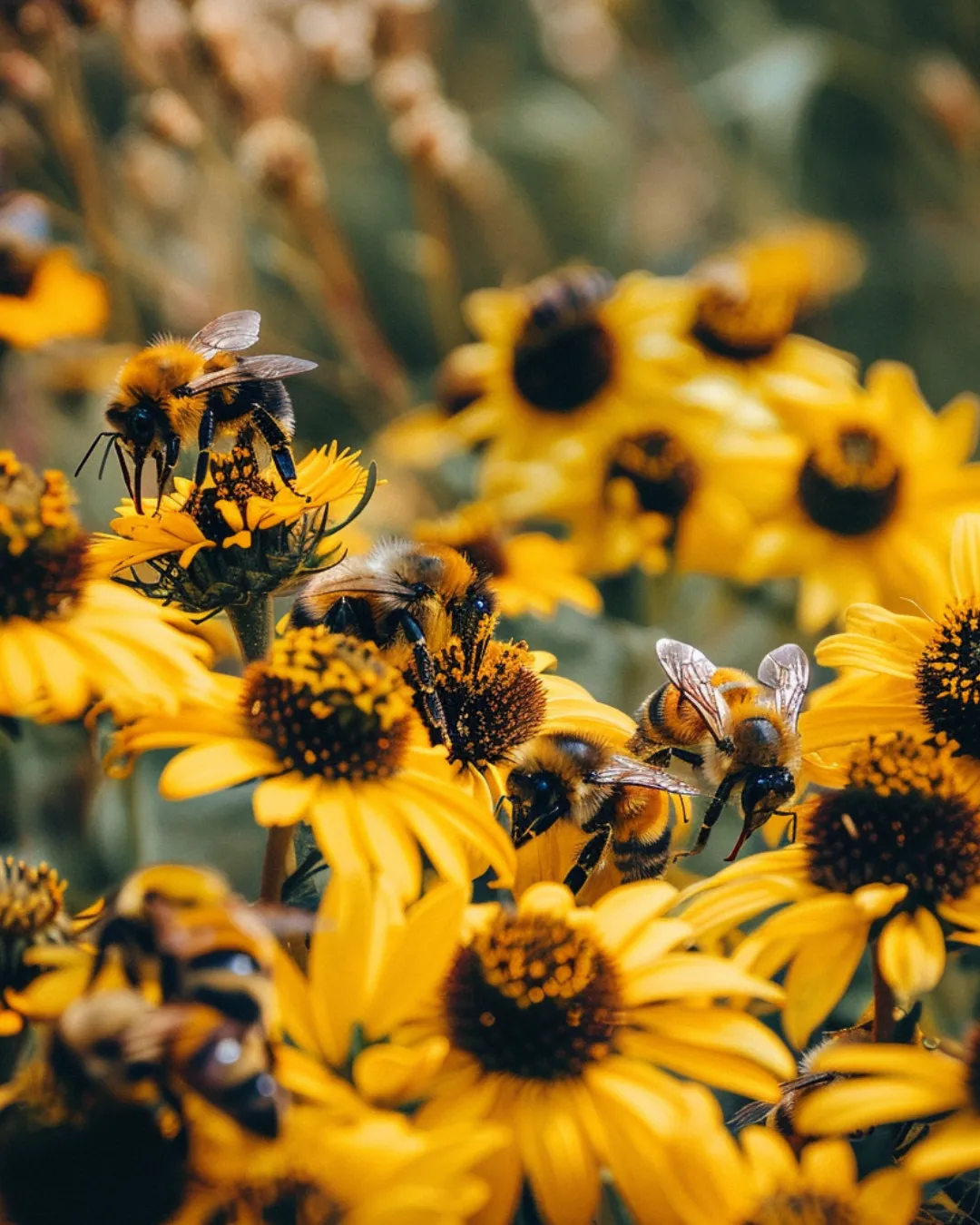

The Buzz on Bees: Importance and Safe Management
Understanding the Importance of Bees
Pollination Powerhouses: Bees are among the most effective pollinators on Earth. They contribute to the growth of trees, flowers, and other plants, which serve as food and shelter for wildlife. They are also critical for the pollination of many of the crops that contribute to the world’s food supply.
Biodiversity Supporters: By pollinating a wide variety of plants, bees support the growth of thousands of floral species, maintaining both plant and animal diversity.
Economic Impact: It's estimated that in the United States alone, bees pollinate crops worth over $15 billion each year. Their work bolsters the U.S. economy and ensures a stable food supply.
When Bees Become a Nuisance
Despite their benefits, bees can pose risks when nests are built too close to homes or recreational areas. It’s essential to manage these situations carefully to protect both people and bees.
Safe Management Practices
Identify the Bee Species:
Understanding whether you're dealing with honeybees, bumblebees, or other types can influence the management approach. Honeybees, for example, are generally more beneficial and less aggressive, warranting gentle relocation efforts.
Professional Removal and Relocation:
If you find a bee hive on your property, consider contacting a professional beekeeper or a pest control expert who specializes in non-lethal bee removal. These professionals can safely relocate the hive without harming the bees.
Preventive Measures:
To prevent bees from building a hive in or around your home, ensure that potential nesting spots are sealed. Maintain a clean garden and yard, free from debris and excessive clutter where bees might establish a new colony.
Creating a Bee-Friendly Environment:
Instead of driving bees away, consider supporting them by planting bee-friendly flowers and shrubs. Gardens designed to attract bees can help maintain their populations and support their role in pollination, while keeping them safely distanced from your living spaces.
Educate and Inform:
Educate your family and community about the importance of bees and how to coexist safely with them. Understanding leads to better reactions and safer interactions between humans and bees.
Bee Behavior Insights: Understanding Why Bees Swarm and Nest Near Homes
Understanding the behavior of bees is essential in managing our interactions with them and preventing conflicts. Here’s an overview of why bees might swarm or establish hives near homes and how this knowledge can enhance safety.
Swarming: A Natural Process
Swarming is a natural part of the bee life cycle, occurring typically in the spring. It happens when a bee colony outgrows its hive, and the queen bee leaves with a large group of worker bees to form a new colony. During this process, swarms may temporarily rest in unusual places, like tree branches near homes or even on structures, as scout bees search for a suitable new home. Understanding that swarming is a temporary state can reduce panic and lead to safer outcomes.
Reasons for Nesting Near Homes
Bees may choose to establish a new hive near human habitation for several reasons:
Shelter: Man-made structures often provide ideal sheltered spaces that are less available in nature, such as hollow walls or spaces under roof eaves.
Temperature Regulation: The controlled climates of human dwellings can offer more stable conditions compared to the wild, especially in regions with extreme weather.
Food Sources: Urban gardens, decorative flowering plants, and abundant water sources can attract bees, making residential areas appealing for setting up a hive.
Preventing Unwanted Bee Hives
Inspect and Seal Potential Entrances: Regularly check your home for gaps or openings where bees might enter. Sealing these can prevent bees from establishing a nest within your structures.
Manage Your Garden: While it’s beneficial to plant bee-friendly flowers, it's also wise to manage plant placement and blooming cycles to discourage bees from nesting too close to high-traffic areas.
Water Source Management: Bees need water, but you can manage where they collect it by ensuring that water sources are not too close to your living spaces.
Promoting Safe Coexistence
Education: Educate your family and community about bee behavior. Understanding that bees usually do not attack unless provoked can help people react more calmly and safely around them.
Professional Guidance: If bees have established a hive in or very near to your home, it’s safest to consult with pest control professionals or local beekeepers for advice and removal.
First Aid for Bee Stings: Essential Steps for Safe Management
Bee stings can be painful and, for those with allergies, potentially life-threatening. Knowing how to respond promptly and effectively is crucial for safety. Here’s a guide on how to handle a bee sting, including the removal of a stinger and understanding when to seek medical attention.
Stinger Removal:
Act Quickly: The first step after being stung by a bee is to remove the stinger as quickly as possible. Bee stingers continue to release venom into the skin for several minutes after the sting, so prompt removal reduces the amount of venom injected.
Use a Flat Object: Instead of using tweezers, which can squeeze more venom into the skin, use the edge of a credit card or a fingernail to scrape the stinger away. This method helps to avoid additional venom release.
Immediate Care:
Clean the Area: Once the stinger is removed, clean the sting site with soap and water to prevent infection.
Apply Ice: Reduce swelling and pain by applying a cold pack or ice wrapped in a cloth to the affected area for a few minutes at a time.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be taken to ease the pain. Antihistamines can help manage itching and swelling.
Home Remedies:
Use Baking Soda Paste: For a non-allergic reaction, applying a paste made of baking soda and water can neutralize bee venom and reduce pain, itching, and swelling.
Aloe Vera: The soothing properties of aloe vera can help reduce the pain and swelling associated with bee stings.
Monitoring Symptoms:
Watch for Allergic Reactions: After a bee sting, closely monitor the person for signs of an allergic reaction, which can include hives, swelling in areas of the body away from the sting, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or a rapid pulse. These symptoms may indicate anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction.
Know When to Seek Medical Help: If any symptoms of an allergic reaction occur, seek immediate medical attention. Call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room.
Preventive Measures:
Wear Protective Clothing: If you're in an area with many bees, wear long sleeves, pants, and closed-toe shoes.
Avoid Scented Products: Fragrances in soaps, shampoos, and lotions can attract bees, so it's advisable to use unscented products when planning to spend time outdoors.
Wayne’s Pest Extermination’s Commitment
At Wayne’s Pest Extermination, we recognize the essential role bees play in our ecosystem. We’re committed to promoting their health and safeguarding human activities through informed management and safe removal practices. If you encounter a bee hive and are unsure how to proceed, contact us. We’re here to help assess the situation and recommend the best approach for keeping both your family and our bee populations safe.
For more advice on bee management or to schedule a consultation, visit our website or reach out to our team directly. Together, let's support these vital pollinators who do so much for our world.

Schedule a Pest Inspection
Ready to schedule a pest inspection? Contact us today.